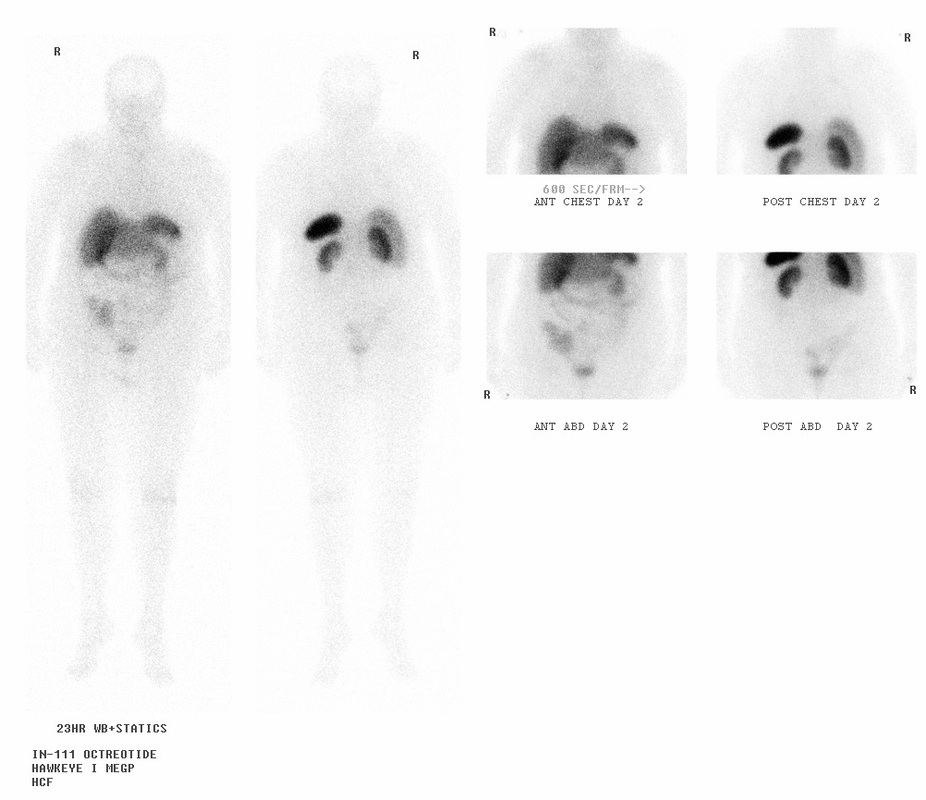
In-111 Pentreotide (OctreoScan)
This radiotracer, which binds preferentially to somatostatin receptor, is used to localize PNET tumors.
Go back to Oncology (Nuclear) imaging.
Go back to Oncology (Nuclear) imaging.
Normal biodistribution
4 hours after tracer injection: Blood pool, normal thyroid, kidneys and bladder, liver, gallbladder, spleen
24 hours after tracer injection: Blood pool, normal thyroid, kidneys and bladder, liver, gallbladder, spleen, and bowel (as seen in the image above)
Image
Courtesy of SLEH
24 hours after tracer injection: Blood pool, normal thyroid, kidneys and bladder, liver, gallbladder, spleen, and bowel (as seen in the image above)
Image
Courtesy of SLEH
Patient Preparation
Octreotide acetate therapy should be discontinued 1 day if standard preparation, or 4 weeks if long acting/slow-release, before In-111 pentetreotide is administered.
Protocol
Notes
Pheochromocytoma has classically hyperintense signal on T2W MR images.
- RM at Endocrinology MDTB in 7/2014
- RM at Endocrinology MDTB in 7/2014