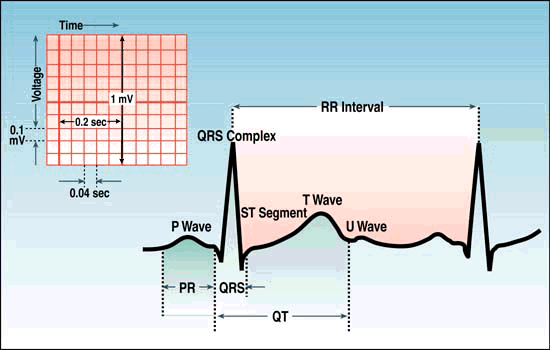
EKG for Nuclear Cardiac Imaging
Source (unless otherwise specified): Dr. F.G. Yanowitz. "ECG Learning Center." Hosted by University of Utah School of Medicine. Link.
Basic Waveform
Heart rate (state atrial and ventricular, if different)
PR interval (from beginning of P to beginning of QRS)
> Normal: 0.12-0.20 seconds
> If < 0.12 seconds, consider pre-excitation syndrome or AV junctional rhythms
> If > 0.20 seconds, consider 1st or 2nd degree AV block (Link)
QRS duration (width of most representative QRS)
> Normal: 0.06-0.12 seconds
> If QRS > 0.12 seconds, consider complete RBBB or LBBB or intraventricular conduction delay (Link)
QT interval (from beginning of QRS to end of T)
QRS axis in frontal plane (go to: "How To Determine Axis")
Go to: ECG Measurement Abnormalities (Lesson IV) for description of normal and abnormal measurements
PR interval (from beginning of P to beginning of QRS)
> Normal: 0.12-0.20 seconds
> If < 0.12 seconds, consider pre-excitation syndrome or AV junctional rhythms
> If > 0.20 seconds, consider 1st or 2nd degree AV block (Link)
QRS duration (width of most representative QRS)
> Normal: 0.06-0.12 seconds
> If QRS > 0.12 seconds, consider complete RBBB or LBBB or intraventricular conduction delay (Link)
QT interval (from beginning of QRS to end of T)
QRS axis in frontal plane (go to: "How To Determine Axis")
Go to: ECG Measurement Abnormalities (Lesson IV) for description of normal and abnormal measurements
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH)
General Features (Link):
> QRS amplitude (voltage criteria; i.e., tall R-waves in LV leads, deep S-waves in RV leads)
Delayed intrinsicoid deflection in V6 (i.e., time from QRS onset to peak R is >0.05 sec)
Widened QRS/T angle (i.e., left ventricular strain pattern, or ST-T oriented opposite to QRS direction)
Leftward shift in frontal plane QRS axis
Evidence for left atrial enlargement (LAE) (lessonVII)
General Features (Link):
> QRS amplitude (voltage criteria; i.e., tall R-waves in LV leads, deep S-waves in RV leads)
Delayed intrinsicoid deflection in V6 (i.e., time from QRS onset to peak R is >0.05 sec)
Widened QRS/T angle (i.e., left ventricular strain pattern, or ST-T oriented opposite to QRS direction)
Leftward shift in frontal plane QRS axis
Evidence for left atrial enlargement (LAE) (lessonVII)
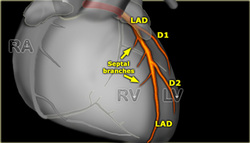
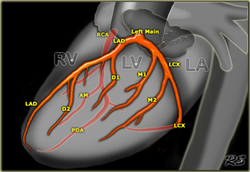
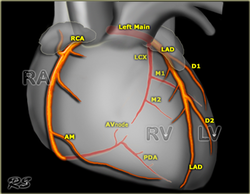
Coronary Artery Map
Below are images showing common distribution of the main coronary arteries.
Left anterior descending (LAD)
Left Circumflex (LCx)
Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
Source
Smithuis R and Willems T. Coronary anatomy and anomalies. The Radiology Assistant. Date unlisted.
Smithuis R and Willems T. Coronary anatomy and anomalies. The Radiology Assistant. Date unlisted.